- Correct and accurate knowledge on various aspects of RFID
- Simple and easy-to-understand presentation of knowledge on RFID with examples from daily life
- Opportunity to discuss and learn more about RFID from our experts
I believe to provide correct and accurate knowledge, it is important to start from the basics. With RFID and Barcode being used extensively in conversations (many a times, interchangeably), we believe we should make an attempt to educate our users on the difference between Barcode and RFID. We will do so in an easy-to-understand manner as promised.
What is a barcode?
Imagine standing in a queue at a supermarket. You may have bought a lot of things. You reach the teller after standing in the queue for quite a while. The teller holds the bar code scanner in his hand and swiftly fetches the pricing data for each item. The price of each item is captured in the computer in front of him and he gives you a final bill within minutes.
If one of the items cannot be scanned, you may have to go back into the supermarket and fetch another unit of the same thing.
What was being used here and how was the data read? Every item that you put into your cart has an attached barcode. A barcode is a series of black lines with data stored in them. The scanner that the teller places on the barcode reads this data and converts it into a numerical equivalent which you see on the tellers screen.
Now, consider a warehouse which has 400 boxes of goods. Is it possible to tag each item with a barcode? Then, when the data has to be read, scan each box with a barcode and collect the data. It is possible for sure but the question to be asked is – Is it efficient?
Wouldn’t it be easier if there was a mechanism which could transmit data stored on or in each of these boxes and a reader could collect the data much faster?
That is exactly where RFID comes in.
Tell me a bit more – How does RFID work?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) uses radio waves to retrieve the data stored in a tiny circuitry on each object. The circuit is neatly stored with protection (often in the goods/ tagged item). Radio waves can pass through solid objects, meaning no line of sight is necessary in getting the data. Since line of sight is not required (you do not need to hold the scanner right on top of the RFID tag on the object to scan data), the process is automated and can read anywhere between 40 to 100 tags in a second.
Imagine the power of this technology by thinking that you bought about 50 items in a supermarket and it was placed on the counter. Your happiness would multiply if the items were scanned in 2 seconds and the bill was ready for you. Won’t it?
Over and above the obvious efficiency advantage, there is a lot more that distinguishes RFID from barcodes. A gist is as below:
Advantages of RFID over Barcode
- No Line-of-sight required to read Data
- Simultaneous and multiple Tag reads – 10’s to 1000’s within seconds
- Works in harsh environments(compared to bar-code / optical technologies
- Can be read through clothing and non-metal items thus negating need to open boxes for counting
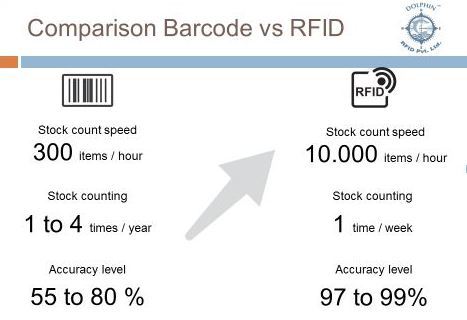
The advantages of RFID in a scenario like a warehouse are best illustrated as follows: